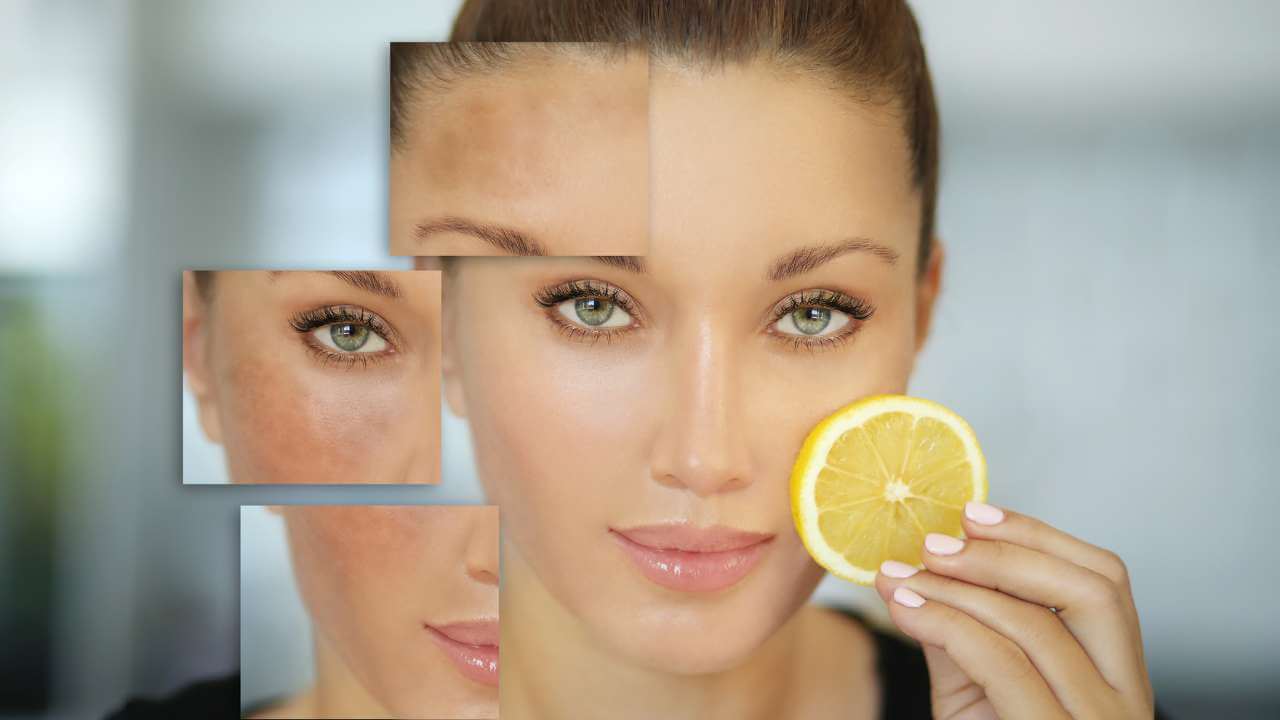
Are you tired of dealing with hyperpigmentation and looking for a solution that can help you achieve healthy and glowing skin? Well, look no further because vitamin C might be the answer you've been searching for!
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin concern that affects individuals of all ages and skin types. It is caused by various factors such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, and skin injuries, and can be challenging to treat.
But what if we told you that vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant, could potentially help with this issue?
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the wonders of vitamin C for treating hyperpigmentation and how it works to give you the skin you've always dreamed of.
We'll dive into the benefits of vitamin C for skin health, its role in the removal of dead skin cells, and why it's an excellent choice for individuals with oily skin and sensitive skin.
So, whether you're dealing with dark patches, age spots, or acne scars, keep reading to discover how vitamin C can help you achieve the healthy, glowing skin you deserve.
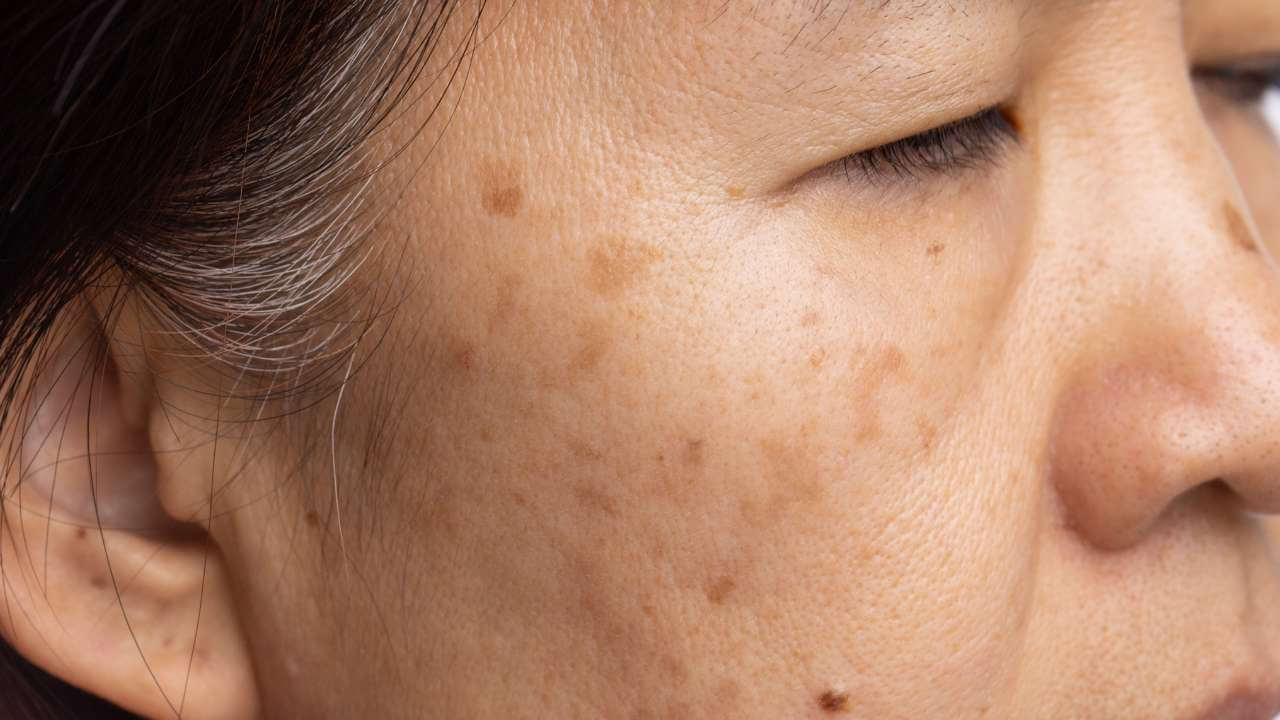
What Is Hyperpigmentation?
Have you ever noticed dark spots or patches on your skin that seem to appear out of nowhere? Well, you might be experiencing hyperpigmentation.
Our skin color is primarily due to melanocytes, which produce melanin, a pigment that absorbs and scatters UV radiation to protect our skin from sun damage.[1]
Melanocytes are constantly activated or resting, depending on sun exposure, and excessive sun exposure can cause them to multiply, resulting in uneven distribution and excess melanin production in the skin.
This overproduction of melanin can lead to hyperpigmentation, which is characterized by the formation of dark patches and spots on the skin.[2]
Hyperpigmentation is more common during warm months when the sun and heat trigger inflammation and increase melanin activity.
While it's difficult to remove hyperpigmentation completely, incorporating vitamin C treatments into your daily skin ritual can help to protect your skin from further damage.
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that not only helps to reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation but also promotes collagen production, which is essential for maintaining healthy skin.[3]
It's essential to consider skin sensitivity when choosing a vitamin C product, as some products can cause irritation, redness, and inflammation. Consulting with a dermatologist and selecting a product that is suitable for your skin type is crucial to achieving the best results.
Excessive melanin production can lead to hyperpigmentation, which can be a significant cosmetic concern for many individuals.
However, by protecting your skin from further damage and incorporating vitamin C treatments into your daily skincare routine, you can achieve healthy, glowing skin and reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation.

What is Vitamin C?
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in many bodily functions.[4] It is an essential nutrient that cannot be produced by the body, so it must be obtained through diet or supplements.
Vitamin C acts as an antioxidant and helps protect skin cells from the damaging effects of free radicals. It is also necessary for the production of collagen, which is a protein that supports skin health, and it aids in the absorption of iron from plant-based foods.
Vitamin C has been shown to provide many health benefits, including boosting the immune system, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and improving skin health.
It is a popular ingredient in skincare products due to its ability to brighten and even out skin tone, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and protect against environmental damage.
Let's discuss the benefits of Vitamin C in more detail.
Benefits of Vitamin C for Skin Tone
- May Protect Against Sun Damage: Vitamin C may have protective benefits against the damaging effects of UV light due to its antioxidant properties. However, it should be noted that vitamin C is not a substitute for sunscreen, as it does not absorb UVA or UVB rays. While it can't replace SPF, studies indicate that vitamin C may be beneficial in reducing the harmful effects of UV light on the skin.[5]
- Anti-Aging Properties: Vitamin C has anti-aging benefits when applied topically through creams or lotions.[6] It protects the skin from harmful UV rays, pollution, and free radicals present in the air, helping to slow down the natural aging process. Its antioxidant properties act as a shield against the constant assaults of the environment, making it a valuable tool in protecting the skin. Vitamin C can be instrumental in maintaining youthful-looking, healthy skin by aiding collagen production, which is essential for skin elasticity and firmness.
- Replenishes Vitamin E: Vitamin C has an additional function as the main replenisher of vitamin E besides its well-known anti-aging and photoprotective properties.[6] Vitamin E is a type of antioxidant that is lipophilic in nature and plays a crucial role in safeguarding cell membranes from oxidative stress, as well as preserving the skin's collagen network.
- Lightening Dark Spots: Vitamin C-based skin care products have been shown to lighten pigmentation patches on the skin.[6] A study found that applying vitamin C to the skin for 16 weeks significantly reduced the appearance of these spots. However, further research is needed to confirm the effectiveness of vitamin C creams.
- Smoothing Wrinkles: Vitamin C is a powerful ingredient in many anti-aging products. Studies suggest that it can reduce the appearance of wrinkles when used for at least 12 weeks.[7] Eating a healthy diet high in this nutrient can also help. People who consume more vitamin C tend to have fewer wrinkles.
- Boosting Collagen Production: Vitamin C encourages new collagen production while also maintaining existing collagen and protecting it from damage.[8] Collagen is essential to support skin elasticity and firmness. Learn more about the anti-aging benefits of collagen including the top picks for the best supplement with our complete guide.
- Reducing Redness & Evening Skin Tone: Vitamin C has anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce puffiness and redness on the skin. It helps neutralize free radicals that cause oxidative damage and optimize the immune system to discourage an inflammatory immune response. Its anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce redness caused by damage to the skin’s protective barrier and create a more even and glowing complexion.
- Fading Hyperpigmentation: Vitamin C can inhibit melanin production, which can fade hyperpigmentation including sunspots, age spots, and melasma.[9] It’s widely used in dermatology for reducing pigmentation of hyperpigmented spots on the skin.
- Wound Healing: Topical application of vitamin C can speed up overall wound healing, reducing the risk of inflammation, infection, and scarring. Vitamin C boosts collagen production, which is associated with wound healing. Studies have found that taking vitamin C supplements had a positive effect on skin healing and growth by boosting antioxidant levels in the body and the skin.[10]
- Safety Profile: Vitamin C is an incredibly safe ingredient, which can be used topically and over long durations by nearly everyone without the risk of unpleasant consequences. It's even safe when combined with other skin protection products like retinol, alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), and sunscreens!
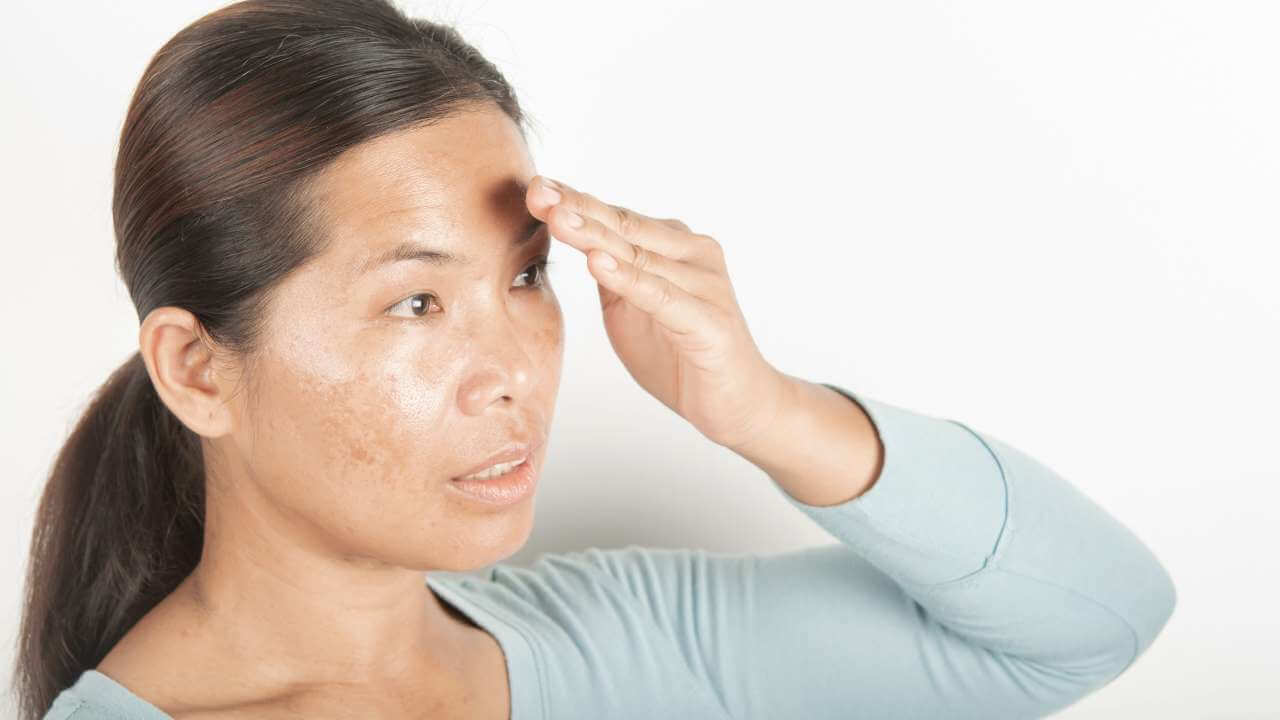

Symptoms and Types of Hyperpigmentation
There are various types and symptoms of hyperpigmentation which may vary in severity depending on the underlying cause.
Understanding the different types and symptoms can help you determine the best course of action for treating your hyperpigmentation.
The most common types of hyperpigmentation include:
- Age Spots: Age spots, also known as liver spots or solar lentigines, are brown, tan, or black spots that appear on the skin due to sun overexposure.[11] They usually appear on the skin around the mouth, face, and hands, or sun-exposed areas of the body. Age spots are commonly found in older adults or those with extended sun exposure.
- Melasma: Melasma, also known as chloasma or "the mask of pregnancy," appears on dry skin as discolored patches of darkened skin. It is often found on the forehead, face, and stomach. Melasma usually affects women who are pregnant or taking birth control pills, and those with medium to darker skin.[12]
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation: Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is characterized by spots or patches of darker skin that appear after an inflammatory skin condition, such as acne or eczema. This type of hyperpigmentation can appear anywhere on the body and is commonly found in people who have had inflammation or an injury to the skin.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
While various factors can cause this condition, it is most often caused by sun exposure, hormones, certain medications, and other medical treatments.
Other causes of hyperpigmentation include genetics, inflammation, or injury to the skin. In some cases, an underlying medical condition may be responsible for triggering hyperpigmentation.
Therefore, it’s important to understand what might be causing your particular issue before seeking treatment.
- Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to the sun can cause the body to produce more melanin, leading to dark spots or patches on the skin, commonly known as age spots or sun spots.[13]
- Skin Inflammation: Skin inflammation due to conditions such as acne, eczema, and lupus can cause areas of the skin to darken. Shaving with a dull razor often results in nicks or cuts causing injury to the skin that can also result in darker skin pigmentation.
- Medications: Certain medications such as antimalarials to antiretrovirals drugs can cause hyperpigmentation, and in such cases, patches of skin may turn gray.[14] Chemicals in topical treatments can also sometimes cause hyperpigmentation.
- Melasma and Pregnancy: The change in hormones during pregnancy or when using birth control pills can trigger it.[12] Melasma usually disappears after pregnancy or when the person stops taking birth control pills. If it does not fade, a board-certified dermatologist may recommend avoiding sun exposure, using topical creams that contain zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, or iron oxide, or undergoing procedures such as chemical peels, micro-needling, laser, or light treatments.
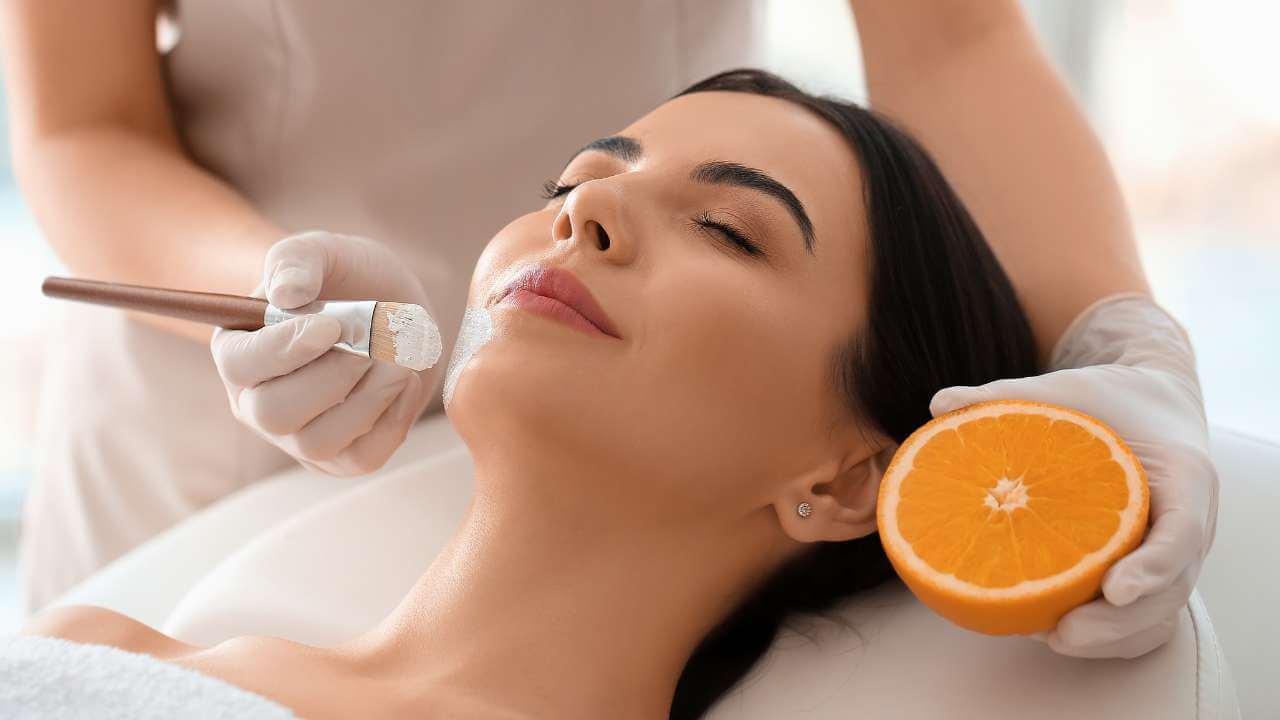
How to Integrate Vitamin C Into Your Skin Care Routine?
Vitamin C is a powerhouse ingredient in skincare that has been shown to promote collagen production, reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation, and improve overall skin health.
However, with so many vitamin C products on the market, it can be overwhelming to choose the right one and incorporate it into your daily skincare routine, especially if you have sensitive skin.
One popular option is introducing topical vitamin C in your skin care routine, which can come in the form of serums, moisturizers, face masks, and eye creams.
When choosing a vitamin C product, it's essential to look for ascorbic acid, which is the most effective form of vitamin C for skincare.
- Vitamin C Serum: Topical Vitamin C serums are an excellent option for targeting hyperpigmentation, sun damage, and uneven skin tone. Ascorbic acid is the most effective form of Vitamin C for skincare, and you should look for a serum with a concentration of at least 10% for maximum benefits. For the best vitamin C serum, we recommend ones that also contain mulberry extract for added health benefits. It's recommended to apply the serum after cleansing and toning and before moisturizing, both in the morning and at night.
- Vitamin C Moisturizers: Vitamin C moisturizers are a great option for those with dry or sensitive skin. They can provide hydration while also targeting hyperpigmentation and uneven skin tone. As with serums, it's important to look for a moisturizer with ascorbic acid and apply it after cleansing and toning. For those with oily skin, a lightweight formula is recommended.
- Vitamin C Face Masks: Vitamin C face masks are an excellent way to give your skin an extra boost of hydration and brightening. You can try to make your own DIY turmeric mask that is rich in vitamin C, or look for a store-bought mask with a high concentration of ascorbic acid. Use it once a week after cleansing and toning and leave it on for the recommended time before rinsing off with warm water.
- Vitamin C Eye Creams: The best vitamin C eye creams are designed to target fine lines, wrinkles, and dark circles around the delicate eye area. Look for a formula that includes ascorbic acid, and gently tap it into the skin with your ring finger after cleansing and toning.
- Vitamin C Face Wash: Vitamin C face washes are an excellent option for those who want to incorporate vitamin C into their daily routine. Look for a face wash with ascorbic acid, and use it twice daily for the best results.
In addition to these topical treatments, there are cosmetic procedures that can also help reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation. These procedures include:
- Laser Therapy
- Intense Pulsed Light
- Chemical Peels
It is important to consult with a dermatologist or skin care specialist before deciding to undergo any of these procedures, as they can potentially worsen hyperpigmentation by damaging the outer layer of the skin.
Common Forms of Vitamin C and its Uses in Skincare
Ascorbic Acid
Ascorbic Acid (L-Ascorbic Acid) is the purest and most efficient form of vitamin C. It has proven to suppress melanin formation, making it a widely used ingredient in skin depigmentation products.
Furthermore, ascorbic acid also protects against UV radiation even after sun exposure since topical treatments have been seen to reduce inflammatory reactions.
Additionally, this powerful derivative can be utilized for reducing age spots, melasma, stretch marks, and other similar issues at deeper levels of the skin.
Vitamin C Derivatives
Vitamin C is renowned for its antioxidant properties, though it tends to quickly break down when exposed to light or air. To combat this natural decomposition, several derivatives of vitamin C are utilized in skin health applications.
The addition of compounds like phosphate and palmitate provides a protective barrier against degradation while also creating effective skincare formulations.
When compared to ascorbic acid, derivatives of vitamin C can be more stable and not as prone to light or air exposure. They may cause less irritation on the skin's surface and are not dependent on pH levels; though it must be noted that these derivatives tend to be slightly less effective.
Popular examples include magnesium ascorbyl palmitate, calcium ascorbate, etc. Knowing their characteristics is crucial for getting the most out of your Vitamin C skincare products!
Ascorbyl Palmitate
Ascorbyl Palmitate, often referred to as Vitamin C ester, is a unique oil-soluble derivative that quickly penetrates the skin layers and converts into ascorbic acid upon application. This form of vitamin C is more stable than its predecessor when used topically which makes it an excellent choice for those looking to improve their skincare routine.
Ascorbyl Glucoside
Ascorbyl Glucoside is an exceptionally stable derivative of vitamin C, making it optimal for those with sensitive skin types. When used topically on the skin, this component quickly converts to ascorbic acid--allowing users to experience its nourishing effects almost immediately!
Ascorbyl Tetraisopalmitate
Ascorbyl Tetraisopalmitate is an oil-soluble form of vitamin C that remains stable at a pH level lower than 5. Applied to the skin, it transitions into ascorbic acid and penetrates more effectively than other derivatives.
Important Facts About Vitamin C and Hyperpigmentation
- Not All Vitamin C Products Are Created Equal: Vitamin C products differ in concentration levels, active ingredients, and chemical structure. Ascorbic acid is the purest and most effective variant of vitamin C, but it rapidly oxidizes and can cause skin irritation. It's essential to avoid formulations containing harmful ingredients like parabens, petrochemicals, synthetic colorants, and artificial fragrances. Choose products with medical-grade ingredients and naturally certified formulas.
- Vitamin C Doesn't Cause Skin Discoloration, It Can Even Out Skin Tone: Vitamin C evens out the skin tone and brightens it over time, but exposure to light and air can degrade the product, turning it brown/orange and rendering it ineffective. It's recommended to use L-ascorbic acid skin products within three months.
- Vitamin C's Efficiency is Dependent on Specific Formulation, Not Percentage Levels: The effectiveness of vitamin C is dependent on pH levels and specific formulations rather than the concentration percentage. While a percentage range of 10% to 20% is considered safe to use, it's advisable to opt for lower percentages as the absorption factor makes the difference.
Did We Mention...
Vitamin C Hyperpigmentation FAQs?
Many people have questions about vitamin C and its use in skincare. It can be overwhelming to navigate through the myths and facts about this popular ingredient, especially with the multitude of products available in the market.
That's why we have put together a list of frequently asked questions about vitamin C for skincare, so that you can have a better understanding of this ingredient and its benefits.
In this section, you will find answers to some of the most commonly asked questions about vitamin C for skincare, such as its precautions, side effects, and usage.
We hope this information will help you make an informed decision about incorporating vitamin C into your skincare routine.
How Does Vitamin C Inhibit Melanin Production?
Vitamin C inhibits the production of melanin by downregulating the activity of an enzyme called tyrosinase. This is achieved through its antioxidant properties, as it neutralizes free radical damage that causes oxidative damage and optimizes the immune system to discourage an inflammatory immune response.
This process is widely used in dermatology to reduce the pigmentation of hyperpigmented spots on the skin. It can also be used to treat gum hyperpigmentation (gingival melanin hyperpigmentation), the exact mechanisms of its action in this context are still under investigation.
What are the Ingredients that Complement Vitamin C for Skincare?
Several products complement Vitamin C for skincare, including sunscreen, vitamin E, and Ferulic Acid. The combination of Vitamin C and sunscreen helps improve sun protection capabilities to fight against skin aging much more effectively.
Vitamin E works together with vitamin C to enhance protection against UV radiation and free radicals. Ferulic Acid also has antioxidant properties, and when combined with L-ascorbic acid, the most potent form of vitamin C, it increases the effectiveness and lifespan of vitamin C.
Hyaluronic acid is also a remarkable ingredient that works wonders along with vitamin C, keeping the skin hydrated and glowing thanks to its powerful water-binding capacity.
What are the Ingredients to Avoid When Using Vitamin C?
To avoid irritation, it is recommended to not use any exfoliating acids immediately after applying vitamin C. Instead, use vitamin C in the morning and exfoliating acids in the evening on alternate days.
Additionally, it is recommended to avoid using niacinamide in combination with vitamin C as it can inactivate vitamin C if they are both in a water-based product. However, niacinamide can still be used as part of a nighttime skincare routine.
Are There Any Other Natural Ingredients that are Helpful for Hyperpigmentation Other than Vitamin C?
Yes, some natural ingredients may help lighten areas of hyperpigmentation apart from vitamin C. These remedies include:
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera contains aloesin that can inhibit the production of melanin in the skin. A 2017 study indicates that aloe vera capsules can bring much-needed reprieve from melasma during pregnancy.[15]
- Licorice Extracts: Licorice extracts, particularly glabridin, may also lighten hyperpigmentation due to their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and skin-whitening effects.[16]
- Green Tea Extracts: Green tea extracts are also believed to have potential antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that can improve hyperpigmentation, although more research is needed to fully understand their effectiveness.[17] As with any treatment or remedy, it's important to do a patch test first and stop using it if it causes irritation.
Can Hyperpigmentation Affect People of All Skin Types?
Hyperpigmentation can affect people of all skin types, although it is more common in individuals with darker skin tones.[18] People with darker skin have more active melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, which can make them more prone to developing hyperpigmentation.
What Measures can be Taken to Prevent Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation can be prevented or its risk can be reduced by taking the following measures:
- Protect the skin from the sun with a sunscreen of SPF 30 or higher.
- Wear protective clothing when outdoors, including hats and sunglasses.
- Avoiding picking at the skin when there are spots, scabs, or acne.
- Seek professional advice before using creams to lighten dark patches.
Can Vitamin C Cause Reactions on the Skin?
Some forms of vitamin C used in skin care products, such as L-ascorbic acid, are formulated at a low acidic pH of around 3 to 3.5.
This level of acidity can cause a tingling or itching sensation on the skin, similar to that experienced with chemical peels.
If this occurs, it is recommended to lower the frequency of use until the skin adjusts and the discomfort subsides.
How Can You Tell if Your Vitamin C Serum is Still Effective?
If your vitamin C serum changes color, it may indicate that it has oxidized and is no longer as effective, according to experts. The product's lively golden color may turn to an orange-brown color, indicating that it may not be delivering the advertised amount of vitamin C.
Additionally, the packaging of the product can also affect its stability. Vitamin C products in tinted or colored glass are typically more stable, as long as the container is airtight as exposure to air can accelerate oxidation.
Opting for an airtight pump instead of a dropper bottle may help the product last longer and be more effective.
Can Hyperpigmentation be a Sign of an Underlying Medical Condition?
In some cases, hyperpigmentation can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as Addison's disease, Cushing's syndrome, or hemochromatosis.[19] If you notice sudden or unusual changes in your skin color, it is important to consult a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying health issues.

The Final Mention
Thank you for reading this comprehensive guide on the benefit of using vitamin C for your skin. We hope that this information has been helpful and has shed light on the many ways that vitamin C can improve your skin's health and appearance.
Remember that vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that can protect your skin from environmental stressors, prevent premature aging, and promote collagen production. It can also help to brighten your skin and reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation.
As with any skincare product, it's important to do your research and choose high-quality, reputable brands that use safe and effective ingredients. Be sure to test any new product on a small patch of skin before using it all over your face and discontinue use if you experience any adverse reactions.
If you want to stay up-to-date on the latest skincare trends and tips, sign up for our free newsletter. You'll receive regular updates on the best products and techniques to help you achieve your healthiest, most radiant skin.
Thank you again for reading, and here's to your best skin yet!
✅ 19 Sources
HealthMention only uses sources from authoritative and reliable resources, such as peer-reviewed studies, to strengthen the accuracy of our content.
- Cichorek M, Wachulska M, Stasiewicz A, Tymińska A. Skin melanocytes: biology and development. Advances in Dermatology and Allergology. 2013;30(1):30-41. doi:https://doi.org/10.5114/pdia.2013.33376
- Davis EC, Callender VD. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: a review of the epidemiology, clinical features, and treatment options in skin of color. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology. 2010;3(7):20-31. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2921758/
- Jm P, Ac C, Mcm V. The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health. Nutrients. Published August 12, 2017. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28805671/
- Abdullah M, Jamil RT, Attia FN. Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid). PubMed. Published 2020. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29763052/
- Darr D, Dunston S, Faust H, Pinnell S. Effectiveness of antioxidants (vitamin C and E) with and without sunscreens as topical photoprotectants. Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 1996;76(4):264-268. doi:https://doi.org/10.2340/0001555576264268
- Al-Niaimi F, Chiang NYZ. Topical Vitamin C and the Skin: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Applications. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology. 2017;10(7):14-17. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5605218/
- Lee C, Yang H, Kim S, et al. Evaluation of the anti-wrinkle effect of an ascorbic acid-loaded dissolving microneedle patch via a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. International Journal of Cosmetic Science. 2016;38(4):375-381. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/ics.12299
- DePhillipo NN, Aman ZS, Kennedy MI, Begley JP, Moatshe G, LaPrade RF. Efficacy of Vitamin C Supplementation on Collagen Synthesis and Oxidative Stress After Musculoskeletal Injuries: A Systematic Review. Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine. 2018;6(10):232596711880454. doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/2325967118804544
- Sanadi RM, Deshmukh RS. The effect of Vitamin C on melanin pigmentation – A systematic review. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology : JOMFP. 2020;24(2):374-382. doi:https://doi.org/10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_207_20
- Moores J. Vitamin C: a wound healing perspective. British Journal of Community Nursing. 2013;18(Sup12):S6-S11. doi:https://doi.org/10.12968/bjcn.2013.18.sup12.s6
- Choi W, Yin L, Smuda C, Batzer J, Hearing VJ, Kolbe L. Molecular and histological characterization of age spots. Experimental Dermatology. 2017;26(3):242-248. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.13203
- Basit H, Godse KV, Al Aboud AM. Melasma. PubMed. Published 2023. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29083744
- Veierod MB, Weiderpass E, Thorn M, et al. A Prospective Study of Pigmentation, Sun Exposure, and Risk of Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma in Women. JNCI Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 2003;95(20):1530-1538. doi:https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djg075
- Hassan S, Zhou X. Drug Induced Pigmentation. PubMed. Published 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542253/
- Ghafarzadeh M, Eatemadi A. Clinical efficacy of liposome-encapsulated Aloe vera on melasma treatment during pregnancy. Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy. 2017;19(3):181-187. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/14764172.2017.1279329
- Ciganović P, Jakimiuk K, Tomczyk M, Zovko Končić M. Glycerolic Licorice Extracts as Active Cosmeceutical Ingredients: Extraction Optimization, Chemical Characterization, and Biological Activity. Antioxidants. 2019;8(10):445. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8100445
- Hollinger JC, Angra K, Halder RM. Are Natural Ingredients Effective in the Management of Hyperpigmentation? A Systematic Review. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology. 2018;11(2):28-37. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5843359/
- Vashi NA, Wirya SA, Inyang M, Kundu RV. Facial Hyperpigmentation in Skin of Color: Special Considerations and Treatment. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology. 2016;18(2):215-230. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-016-0239-8
- Mulligan TM, Sowers JR. Hyperpigmentation, vitiligo, and Addison’s disease. Cutis. 1985;36(4):317-318, 322. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2998703/









